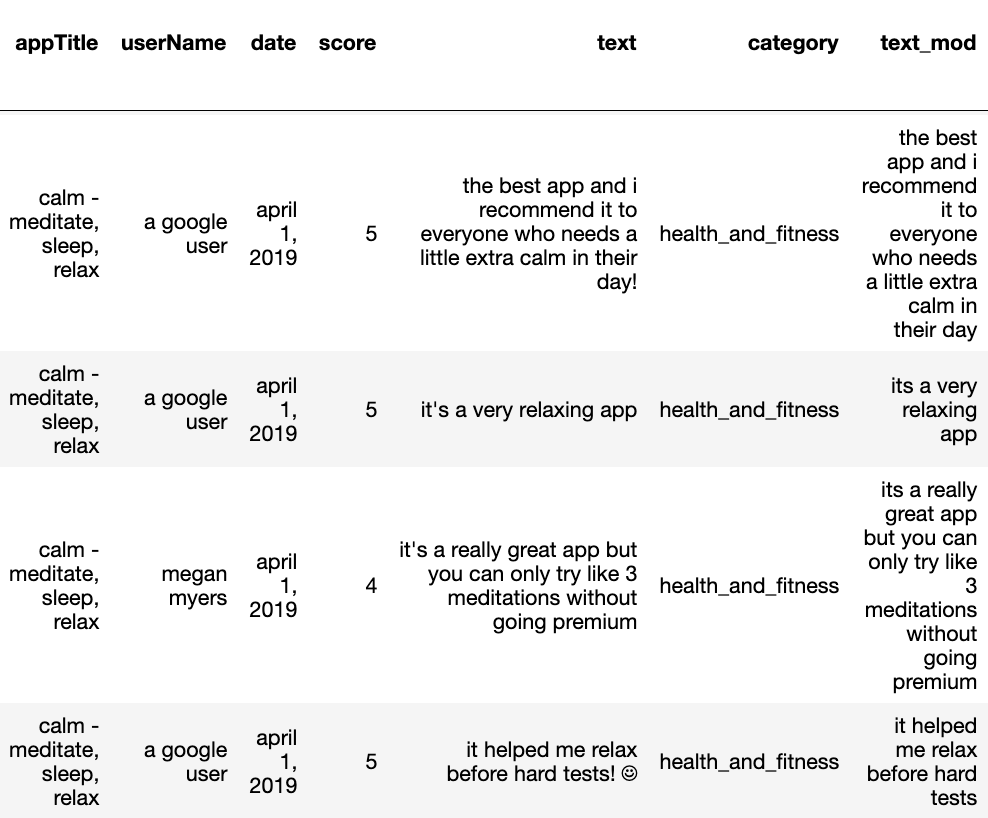
The project’s purpose is to clean and manipulate text data prior to applying machine learning techniques. The dataset contains errors to simulate data collection in the real world.
Dataset Description
Two csv files are collected for mobile applications each week. One csv file includes application reviews, and the other file includes application details. I’m only interested in the reviews csv files.
The datasets are collected for approximately 80 mobile applications. The datasets live on a Google Drive here.
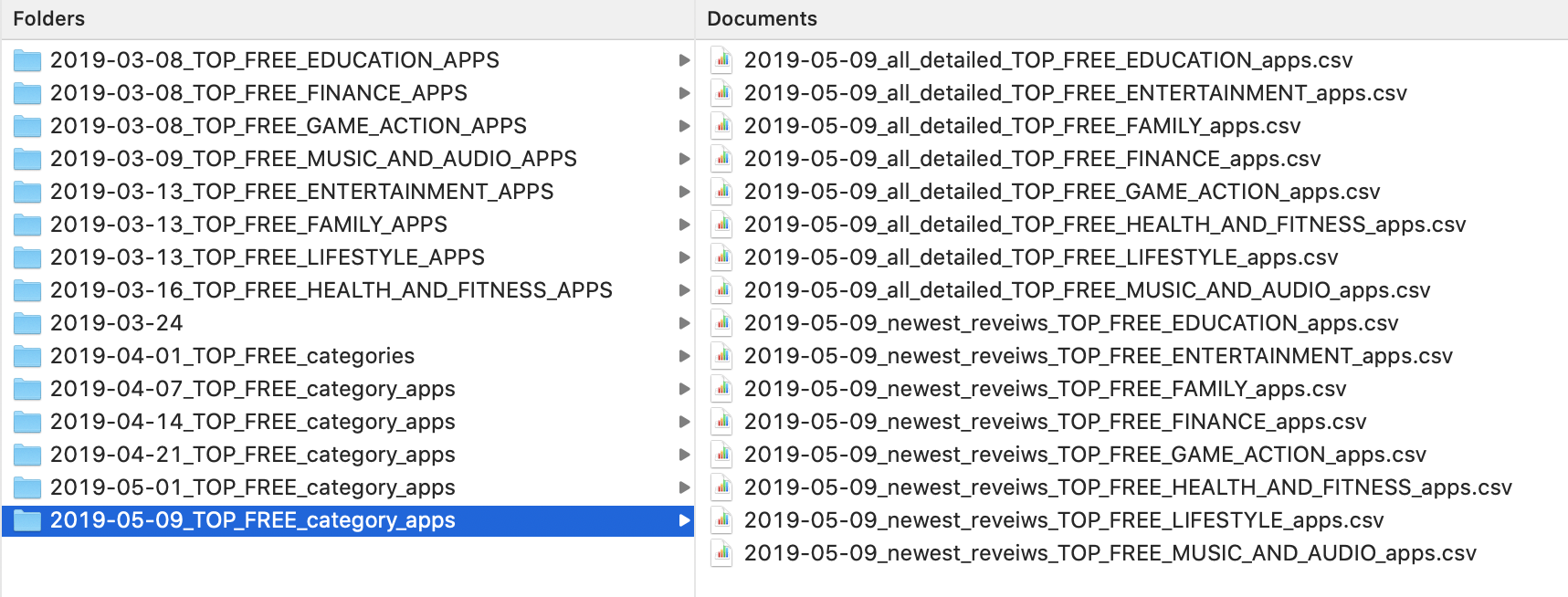
Below is a sample screenshot of the datasets’ file structure after downloading it from Google Drive. The dates represents when the data was pulled from the Google Play Store.
Step 1. Load Relevant Packages and Data
First, import relevant libraries.
1
2
3
4
5
6
import glob
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import nltk
from itertools import groupby
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
The csv files live in multiple folders broken out by dates of data pull. glob makes it easy to only pull review filenames from each folder. Some filenames had ‘reviews’ misspelled as ‘reveiws’, which required two glob commands.
1
2
3
4
files1=glob.glob('/Dataset/**/*reveiws*.csv', recursive=True)
files2=glob.glob('/Dataset/**/*reviews*.csv', recursive=True)
files_total=files1+files2
I create an empty list, read each csv into a data frame, and append each data frame into the list.
1
2
3
4
5
list1 = []
for file_ in files_total:
df1 = pd.read_csv(file_,index_col=None, header=0)
list1.append(df1)
I want to label each app by their categories name. I will need to get the categories name from the filename using split and __contains__.
Some of the filenames have different naming conventions, which required the first two complicated clauses in the if statement.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
categories=[]
for i in range(0,len(files_total)):
if (files_total[i][-40:].split("_",3)[-1].__contains__('FREE')) & ((files_total[i][-40:].split("_",3)[-1].__contains__('TOP_FREE')==False)) :
categories.append(files_total[i][-40:].split("_",4)[-1][:-9])
elif files_total[i][-40:].split("_",3)[-1].__contains__('TOP_FREE'):
categories.append(files_total[i][-40:].split("_",5)[-1][:-9])
else:
categories.append(files_total[i][-40:].split("_",3)[-1][:-9])
After retrieving the categories name I add it to the data frames within the list.
1
2
for i in range(0,len(files_total)):
list1[i]['category']= categories[i]
Merge all the reviews files into one data frame using pandas concat.
1
2
for file_ in files_total:
review_df = pd.concat(list1)
I convert all the string fields to lowercase for aggregation later.
1
review_df=review_df.apply(lambda x: x.astype(str).str.lower())
Drop all duplicate rows.
1
2
review_df=review_df.drop_duplicates()
without_duplicates=len(review_df)
I add a unique ID index to the data set.
1
2
review_df['uniqueID']=range(1,len(review_df)+1)
review_df=review_df.set_index('uniqueID')
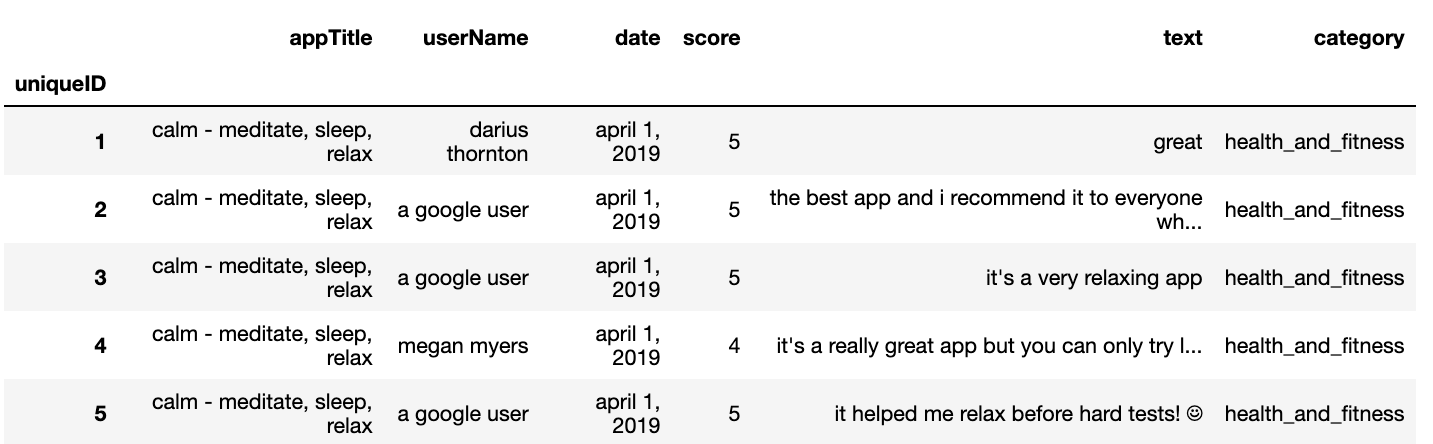
Results of the data frame.
1
review_df.head()
2. Data Manipulation
I create a new column with my text manipulation called “text_mod”.
I remove non-ASCII characters using encode("ascii", "ignore").
1
review_df['text_mod']=review_df['text'].map(lambda x: str(x).encode("ascii", "ignore").decode('utf-8'))
I remove punctuations using regular expressions.
1
review_df['text_mod'] = review_df['text_mod'].str.replace(r'[^\w\s]+', '')
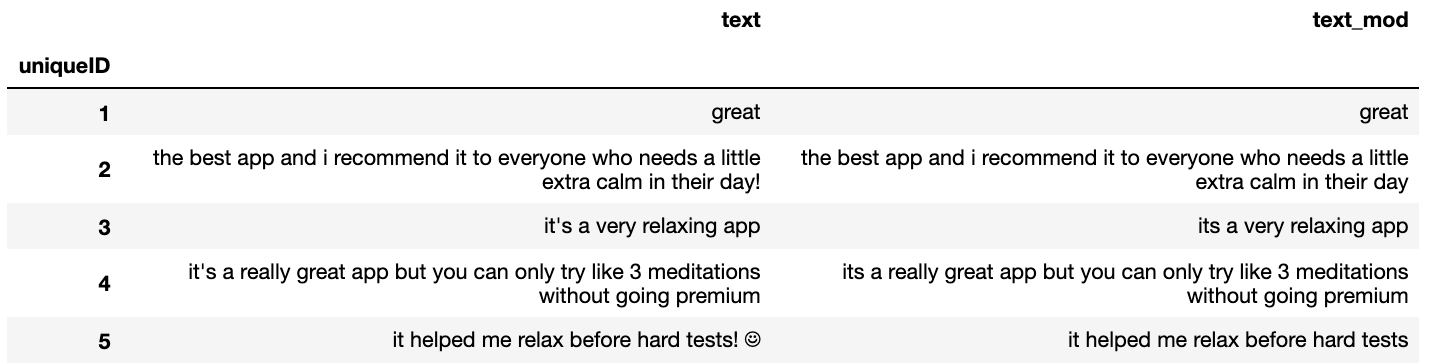
Let’s examine our text processing so far for the first few reviews.
1
2
pd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', None) # this stops the columns from truncating
review_df[['text','text_mod']][0:5]
There are application reviews with slang, emojis, misspelled words, and some are in other languages. I create a function to calculate the ratio of non-English words for each review. If the ratio is higher than 50%, I will label it “NOTENGLISHDROP”, then I drop the review observation with that label (not the entire row).
I use nltk.corpous.words.words() to create an English words dictionary for the comparison. I use nltk.wordpunct_tokenize() to separate each word by a space into a list.
Please note, if you have not downloaded nltk package before, it’ll require an additional command, nltk.download() after importing the package.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
words = set(nltk.corpus.words.words())
def english(string):
wordslist=nltk.wordpunct_tokenize(string)
true_count=0
false_count=0
for w in wordslist:
if w in words or not w.isalpha():
true_count+=1
if w not in words:
false_count+=1
if false_count!=0 or true_count!=0:
if (false_count/(false_count+true_count)>=0.50):
return "NOTENGLISHDROP"
else:
return string
review_df.text_mod=review_df.text_mod.apply(lambda x: english(x))
Below is a sample screenshot of the function applied to the text_mod field.

Now we drop the reviews with the “NOTENGLISHDROP” label by making the text_mod field null.
1
review_df.drop(review_df[review_df.text_mod == 'NOTENGLISHDROP'].index, inplace=True)
Lastly, I remove reviews that contain two or less number of words.
1
2
word_count = review_df['text_mod'].str.split().str.len()
review_df=review_df[~(word_count<=2)]
Final output of our data frame.